HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DRIZALMA SPRINKLE safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DRIZALMA SPRINKLE.
DRIZALMA SPRINKLE™ (duloxetine delayed-release capsules), for oral use.
Initial U.S. Approval: 2004
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
|
|---|
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions (5.5) 6/2020INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DRIZALMA Sprinkle is a serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) indicated for:- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) in adults (1)
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) in adults and pediatric patients ages 7 years to 17 years old (1)
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP) in adults (1)
- Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain in adults (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
| Indication | Starting Dose | Target Dose | Maximum Dose |
|---|---|---|---|
| MDD (2.2) | 40 mg/day to 60 mg/day | Acute Treatment: 40 mg/day (20 mg twice daily) to 60 mg/day (once daily or as 30 mg twice daily); Maintenance Treatment: 60 mg/day | 120 mg/day |
| GAD (2.3) Adults Elderly Children and Adolescents (7 to 17 years old) | 60 mg/day 30 mg/day 30 mg/day | 60 mg/day (once daily) 60 mg/day (once daily) 30 to 60 mg/day (once daily) | 120 mg/day 120 mg/day 120 mg/day |
| DPNP (2.4) | 60 mg/day | 60 mg/day (once daily) | 60 mg/day |
| Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain (2.5) | 30 mg/day | 60 mg/day (once daily) | 60 mg/day |
- Take DRIZALMA Sprinkle with or without food (2.1)
- DRIZALMA Sprinkle may be: swallowed whole (do not crush or chew capsule); opened and sprinkled over applesauce; or administered via nasogastric tube (2.1)
- Take a missed dose as soon as it is remembered. Do not take two doses of DRIZALMA Sprinkle at the same time (2.1)
- There is no evidence that doses greater than 60 mg/day confers additional benefit, while some adverse reactions were observed to be dose-dependent (2)
- Discontinuation: Gradually reduce dosage to avoid discontinuation symptoms (2.9, 5.7)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
20 mg, 30 mg, 40 mg and 60 mg delayed-release capsules (3)CONTRAINDICATIONS
Serotonin Syndrome and MAOIs: Do not use MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with DRIZALMA Sprinkle or within 5 days of stopping treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle. Do not use DRIZALMA Sprinkle within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders. In addition, do not start DRIZALMA Sprinkle in a patient who is being treated with linezolid or intravenous methylene blue (4)WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hepatotoxicity: Hepatic failure, sometimes fatal, has been reported in patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules should be discontinued in patients who develop jaundice or other evidence of clinically significant liver dysfunction and should not be resumed unless another cause can be established. DRIZALMA Sprinkle should not be prescribed to patients with substantial alcohol use or evidence of chronic liver disease (5.2)
- Orthostatic Hypotension, Falls and Syncope: Cases have been reported with duloxetine delayed-release capsules therapy (5.3)
- Serotonin Syndrome: Increased risk when co-administered with other serotonergic agents (e.g., SSRI, SNRI, triptans), but also when taken alone. If it occurs, discontinue DRIZALMA Sprinkle and initiate supportive treatment (5.4)
- Increased Risk of Bleeding: Duloxetine may increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of NSAIDs, aspirin, other antiplatelet drugs, warfarin, and anticoagulants may increase this risk (5.5, 7)
- Severe Skin Reactions: Severe skin reactions, including erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), can occur with duloxetine. DRIZALMA Sprinkle should be discontinued at the first appearance of blisters, peeling rash, mucosal erosions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity if no other etiology can be identified (5.6)
- Discontinuation Syndrome: Taper dose when possible and monitor for discontinuation symptoms (5.7)
- Activation of Mania or Hypomania: Use cautiously in patients with bipolar disorder. Cautions patients about the risk of activation of mania/hypomania (5.8)
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma: Avoid use of antidepressants, including DRIZALMA Sprinkle, in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles (5.9)
- Seizures: Prescribe with care in patients with a history of seizure disorder (5.10)
- Blood Pressure: Monitor blood pressure prior to initiating treatment and periodically throughout treatment (5.11)
- Hyponatremia: Can occur in association with SIADH. Cases of hyponatremia have been reported (5.13)
- Glucose Control in Diabetes: In diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain patients, small increases in fasting blood glucose, and HbA1c have been observed (5.14)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (≥5% and at least twice the incidence of placebo patients): nausea, dry mouth, somnolence, constipation, decreased appetite, and hyperhidrosis (6.1).To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Sun Pharmaceutical Industries, Inc. at 1-800-818-4555 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Potent CYP1A2 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use (2.6, 7)
- CYP2D6 Substrates: Consider dose reduction with concomitant use (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (2.7)
- Renal Impairment: Avoid use in patients with severe renal impairment (2.7, 5.14)
- Pregnancy: Third trimester use may increase risk of symptoms of poor adaptation (respiratory distress, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, hypotonia, tremor, irritability) in the neonate (8.1)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 6/2020
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 2.1 Important Administration Information
- 2.2 Dosage for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
- 2.3 Dosage for Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- 2.4 Dosage for Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
- 2.5 Dosage for Treatment of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
- 2.6 Dosage Recommendations for Concomitant Use with Potent CYP1A2 Inhibitors
- 2.7 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Hepatic and Renal Impairment
- 2.8 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting DRIZALMA Sprinkle
- 2.9 Discontinuation of Treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle
- 2.10 Switching a Patient to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- 5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults
- 5.2 Hepatotoxicity
- 5.3 Orthostatic Hypotension, Falls and Syncope
- 5.4 Serotonin Syndrome
- 5.5 Increased Risk of Bleeding
- 5.6 Severe Skin Reactions
- 5.7 Discontinuation Syndrome
- 5.8 Activation of Mania/Hypomania
- 5.9 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
- 5.10 Seizures
- 5.11 Elevated Blood Pressure
- 5.12 Clinically Important Drug Interactions
- 5.13 Hyponatremia
- 5.14 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
- 5.15 Urinary Hesitation and Retention
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
- 6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
- 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
- 7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with DRIZALMA Sprinkle
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- 8.1 Pregnancy
- 8.2 Lactation
- 8.4 Pediatric Use
- 8.5 Geriatric Use
- 8.6 Gender
- 8.7 Smoking Status
- 8.8 Race
- 8.9 Hepatic Impairment
- 8.10 Severe Renal Impairment
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
- 9.2 Abuse
- 9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
- 10.1 Signs and Symptoms
- 10.2 Management of Overdose
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
- 12.1 Mechanism of Action
- 12.2 Pharmacodynamics
- 12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
- 13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
- 14.1 Major Depressive Disorder
- 14.2 Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- 14.3 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
- 14.4 Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- 16.1 How Supplied
- 16.2 Storage and Handling
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
* Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
| WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behavior in pediatric and young adult patients in short-term studies. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. |
|---|
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DRIZALMA Sprinkle is indicated for the treatment of:- Major Depressive Disorder in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder in adults and pediatric patients 7 years to 17 years old [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]
- Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.4)]
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Information
Administer DRIZALMA Sprinkle with or without food. Swallow DRIZALMA Sprinkle whole (do not chew or crush the capsule). For patients unable to swallow an intact capsule, refer to the alternative administration instructions below. Directions for use with applesauce For patients with swallowing difficulty, DRIZALMA Sprinkle can be opened and the contents sprinkled over applesauce. The contents of the capsules should be swallowed along with a small amount (tablespoonful) of applesauce. The drug/food mixture should be swallowed immediately and not stored for future use. Nasogastric tube administration Open and add contents of capsule to an all plastic catheter tip syringe and add 50 mL of water. Gently shake the syringe for approximately 10 seconds. Promptly deliver through a 12 French or larger nasogastric tube. Ensure no pellets are left in the syringe. Rinse with additional water (about 15 mL) if needed. If a dose of DRIZALMA Sprinkle is missed, take the missed dose as soon as it is remembered. If it is almost time for the next dose, skip the missed dose and take the next dose at the regular time. Do not take two doses of DRIZALMA Sprinkle at the same time.2.2 Dosage for Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
Administer DRIZALMA Sprinkle at a total dose of 40 mg per day (given as 20 mg twice daily) to 60 mg per day (given either once daily or as 30 mg twice daily). For some patients, it may be desirable to start at 30 mg once daily for 1 week, to allow patients to adjust to the medication before increasing to 60 mg once daily. While a 120 mg per day dose was shown to be effective, there is no evidence that doses greater than 60 mg per day confer any additional benefits. The safety of doses above 120 mg per day has not been adequately evaluated. Periodically reassess to determine the need for maintenance treatment and the appropriate dose for such treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].2.3 Dosage for Treatment of Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Adults - For most patients, initiate DRIZALMA Sprinkle 60 mg once daily. For some patients, it may be desirable to start at 30 mg once daily for 1 week, to allow patients to adjust to the medication before increasing to 60 mg once daily. While a 120 mg once daily dose was shown to be effective, there is no evidence that doses greater than 60 mg per day confer additional benefit. Nevertheless, if a decision is made to increase the dose beyond 60 mg once daily, increase dose in increments of 30 mg once daily. The safety of doses above 120 mg once daily has not been adequately evaluated. Periodically reassess to determine the continued need for maintenance treatment and the appropriate dose for such treatment [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Elderly - Initiate DRIZALMA Sprinkle at a dose of 30 mg once daily for 2 weeks before considering an increase to the target dose of 60 mg. Thereafter, patients may benefit from doses above 60 mg once daily. If a decision is made to increase the dose beyond 60 mg once daily, increase dose in increments of 30 mg once daily. The maximum dose studied was 120 mg per day. Safety of doses above 120 mg once daily has not been adequately evaluated [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Children and Adolescents (7 to 17 years of age) - Initiate DRIZALMA Sprinkle at a dose of 30 mg once daily for 2 weeks before considering an increase to 60 mg. The recommended dose range is 30 to 60 mg once daily. Some patients may benefit from doses above 60 mg once daily. If a decision is made to increase the dose beyond 60 mg once daily, increase dose in increments of 30 mg once daily. The maximum dose studied was 120 mg per day. The safety of doses above 120 mg once daily has not been evaluated [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].2.4 Dosage for Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
Administer DRIZALMA Sprinkle 60 mg once daily. There is no evidence that doses higher than 60 mg confer additional significant benefit and the higher dose is clearly less well tolerated [see Clinical Studies (14.3)]. For patients for whom tolerability is a concern, a lower starting dose may be considered. Since diabetes is frequently complicated by renal disease, consider a lower starting dose and gradual increase in dose for patients with renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Use in Specific Populations (8.10), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].2.5 Dosage for Treatment of Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
Administer DRIZALMA Sprinkle 60 mg once daily. Begin treatment at 30 mg for one week, to allow patients to adjust to the medication before increasing to 60 mg once daily. There is no evidence that higher doses confer additional benefit, even in patients who do not respond to a 60 mg dose, and higher doses are associated with a higher rate of adverse reactions [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].2.6 Dosage Recommendations for Concomitant Use with Potent CYP1A2 Inhibitors
Coadministration with potent CYP1A2 Inhibitors: Avoid concomitant use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle with potent CYP1A2 inhibitors.2.7 Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Hepatic and Renal Impairment
Hepatic Impairment: Avoid use in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A), moderate (Child-Pugh B), or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) and Use in Specific Populations (8.9)]. Severe Renal Impairment: Avoid use in patients with severe renal impairment ( CrCl ≥15 to <30 mL/min) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14) and Use in Specific Populations (8.10)].2.8 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting DRIZALMA Sprinkle
Prior to initiating treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle or another antidepressant, screen patients for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].2.9 Discontinuation of Treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle
Adverse reactions may occur upon discontinuation of DRIZALMA Sprinkle [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Gradually reduce the dosage rather than stopping DRIZALMA Sprinkle abruptly whenever possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].2.10 Switching a Patient to or from a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) Intended to Treat Psychiatric Disorders
At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders and initiation of therapy with DRIZALMA Sprinkle. Conversely, at least 5 days should be allowed after stopping DRIZALMA Sprinkle before starting an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
20 mg: hard gelatin capsules with green cap imprinted with “RG53” and green body imprinted with “RG53” containing off-white to pale-yellow colored pellets.
30 mg: hard gelatin capsules with blue cap imprinted with “RG54” and white body imprinted with “RG54” containing off-white to pale-yellow colored pellets.
40 mg: hard gelatin capsules with white cap imprinted with “RL85” and white body imprinted with “RL85” containing off-white to pale-yellow colored pellets.
60 mg: hard gelatin capsules with blue cap imprinted with “RG55” and green body imprinted with “RG55” containing off-white to pale-yellow colored pellets.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Use of MAOIs intended to treat psychiatric disorders with DRIZALMA Sprinkle, or within 5 days of stopping treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle, are contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome. The use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle within 14 days of stopping an MAOI intended to treat psychiatric disorders is also contraindicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.10), Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.12), Drug Interactions (7)]. Starting DRIZALMA Sprinkle in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue is contraindicated because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults
In pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and other antidepressant classes) that included approximately 77,000 adult patients and 4,500 pediatric patients, the incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in the antidepressant-treated patients age 24 years and younger was greater than in placebo-treated patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors among drugs, but there was an increased risk identified in young patients for most drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The drug-placebo differences in the number of cases of suicidal thoughts and behaviors per 1000 patients treated are provided in Table 1.Table 1: Risk Differences of the Number of Patients of Suicidal Thoughts and Behavior in the Pooled Placebo-Controlled Trials of Antidepressants in Pediatric and Adult Patients
| Age Range | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Patients of Suicidal Thoughts or Behaviors per 1000 Patients Treated |
|---|---|
| Increases Compared to Placebo | |
| <18 | 14 additional patients |
| 18 to 24 | 5 additional patients |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo | |
| 25 to 64 | 1 fewer patients |
| ≥65 | 6 fewer patients |
5.2 Hepatotoxicity
There have been reports of hepatic failure, sometimes fatal, in patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules. These cases have presented as hepatitis with abdominal pain, hepatomegaly, and elevation of transaminase levels to more than twenty times the upper limit of normal with or without jaundice, reflecting a mixed or hepatocellular pattern of liver injury. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules should be discontinued in patients who develop jaundice or other evidence of clinically significant liver dysfunction and should not be resumed unless another cause can be established. Cases of cholestatic jaundice with minimal elevation of transaminase levels have also been reported. Other post-marketing reports indicate that elevated transaminases, bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase have occurred in patients with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules increased the risk of elevation of serum transaminase levels in development program clinical trials. Liver transaminase elevations resulted in the discontinuation of 0.3% (92/34,756) of duloxetine delayed-release capsules-treated patients. In most patients, the median time to detection of the transaminase elevation was about two months. In adult placebo-controlled trials in any indication, for patients with normal and abnormal baseline ALT values, elevation of ALT > 3 times the upper limit of normal occurred in 1.25% (144/11,496) of duloxetine delayed-release capsules-treated patients compared to 0.45% (39/8716) of placebo- treated patients. In adult placebo-controlled studies using a fixed dose design, there was evidence of a dose response relationship for ALT and AST elevation of >3 times the upper limit of normal and >5 times the upper limit of normal, respectively. Because it is possible that duloxetine and alcohol may interact to cause liver injury or that duloxetine may aggravate pre-existing liver disease, DRIZALMA Sprinkle should not be prescribed to patients with substantial alcohol use or evidence of chronic liver disease.5.3 Orthostatic Hypotension, Falls and Syncope
Orthostatic hypotension, falls and syncope have been reported with therapeutic doses of duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Syncope and orthostatic hypotension tend to occur within the first week of therapy but can occur at any time during duloxetine delayed-release capsules treatment, particularly after dose increases. The risk of falling appears to be related to the degree of orthostatic decrease in blood pressure as well as other factors that may increase the underlying risk of falls. In an analysis of patients from all placebo-controlled trials, patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules reported a higher rate of falls compared to patients treated with placebo. Risk appears to be related to the presence of orthostatic decrease in blood pressure. The risk of blood pressure decreases may be greater in patients taking concomitant medications that induce orthostatic hypotension (such as anti-hypertensives) or are potent CYP1A2 inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12) and Drug Interactions (7.1)] and in patients taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules at doses above 60 mg daily. Consideration should be given to dose reduction or discontinuation of DRIZALMA Sprinkle in patients who experience symptomatic orthostatic hypotension, falls and/or syncope during duloxetine delayed-release capsules therapy. Risk of falling also appeared to be proportional to a patient’s underlying risk for falls and appeared to increase steadily with age. As elderly patients tend to have a higher underlying risk for falls due to a higher prevalence of risk factors such as use of multiple medications, medical comorbidities and gait disturbances, the impact of increasing age by itself is unclear. Falls with serious consequences including bone fractures and hospitalizations have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].5.4 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and selective-serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), including duloxetine, can precipitate serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk is increased with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, and St. John’s Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)]. Serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone. Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The concomitant use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle with MAOIs is contraindicated. In addition, do not initiate DRIZALMA Sprinkle in a patient who is being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection). If it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules, discontinue duloxetine delayed-release before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7)]. Monitor all patients taking DRIZALMA Sprinkle for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. Discontinue treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle capsules immediately if the above symptoms occur and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome and monitor for symptoms.5.5 Increased Risk of Bleeding
Drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake inhibition, including duloxetine, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), warfarin, and other anti-coagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. A post-marketing study showed a higher incidence of postpartum hemorrhage in mothers taking duloxetine. Other bleeding events related to SSRIs and SNRIs use have ranged from ecchymoses, hematomas, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages. Inform patients about the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle and NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].5.6 Severe Skin Reactions
Severe skin reactions, including erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), can occur with duloxetine. The reporting rate of SJS associated with duloxetine use exceeds the general population background incidence rate for this serious skin reaction (1 to 2 cases per million person years). The reporting rate is generally accepted to be an underestimate due to underreporting. DRIZALMA Sprinkle should be discontinued at the first appearance of blisters, peeling rash, mucosal erosions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity if no other etiology can be identified.5.7 Discontinuation Syndrome
Discontinuation symptoms have been systematically evaluated in patients taking duloxetine. Following abrupt or tapered discontinuation in adult placebo-controlled clinical trials, the following symptoms occurred at 1% or greater and at a significantly higher rate in duloxetine-treated patients compared to those discontinuing from placebo: dizziness, headache, nausea, diarrhea, paresthesia, irritability, vomiting, insomnia, anxiety, hyperhidrosis, and fatigue. Adverse reactions after discontinuation of serotonergic antidepressants, particularly after abrupt discontinuation, include: nausea, sweating, dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesias, such as electric shock sensations), tremor, anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures. Patients should be monitored for these symptoms when discontinuing treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle. A gradual reduction in dosage rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible. If intolerable symptoms occur following a decrease in the dose or upon discontinuation of treatment, then resuming the previously prescribed dose may be considered. Subsequently, the physician may continue decreasing the dose but at a more gradual rate [see Dosage and Administration (2.9)].5.8 Activation of Mania/Hypomania
In patients with bipolar disorder, treating a depressive episode with duloxetine delayed-release capsules or another antidepressant may precipitate a mixed/manic episode. In controlled clinical trials in adult patients with major depressive disorder, patients with bipolar disorder were generally excluded; however, symptoms of mania or hypomania were reported in 0.1% of patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules. No activation of mania or hypomania was reported in DPNP, GAD, or chronic musculoskeletal pain placebo-controlled trials. Prior to initiating treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania.5.9 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs, including duloxetine, may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy. Avoid use of antidepressants, including DRIZALMA Sprinkle, in patients with anatomically narrow angles.5.10 Seizures
Duloxetine has not been systematically evaluated in patients with a seizure disorder, and such patients were excluded from clinical studies. In adult placebo-controlled clinical trials, seizures/convulsions occurred in 0.02% (3/12,722) of patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules and 0.01% (1/9513) of patients treated with placebo. DRIZALMA Sprinkle should be prescribed with care in patients with a history of a seizure disorder.5.11 Elevated Blood Pressure
In adult placebo-controlled clinical trials across indications from baseline to endpoint, duloxetine treatment was associated with mean increases of 0.5 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure and 0.8 mm Hg in diastolic blood pressure compared to mean decreases of 0.6 mm Hg systolic and 0.3 mm Hg diastolic in placebo-treated patients. There was no significant difference in the frequency of sustained (3 consecutive visits) elevated blood pressure. Patients receiving duloxetine delayed-release capsules should have regular monitoring of blood pressure since increases in blood pressure were observed in clinical studies [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Pre-existing hypertension should be controlled before initiating treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle. Caution should be exercised in treating patients with pre-existing hypertension, cardiovascular, or cerebrovascular conditions that might be compromised by increases in blood pressure. Sustained blood pressure increases could have adverse consequences. For patients who experience a sustained increase in blood pressure while receiving DRIZALMA Sprinkle, either dose reduction or discontinuation should be considered [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].5.12 Clinically Important Drug Interactions
Both CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 are responsible for duloxetine metabolism.Potential for Other Drugs to Affect duloxetine delayed-release capsules
CYP1A2 Inhibitors – Avoid concomitant use of duloxetine delayed-release capsules with potent CYP1A2 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. CYP2D6 Inhibitors - Concomitant use of duloxetine delayed-release capsules with potent inhibitors of CYP2D6 would be expected to, and does, result in higher concentrations (on average of 60%) of duloxetine [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].Potential for Duloxetine to Affect Other Drugs
Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6 - Co-administration of duloxetine with drugs that are extensively metabolized by CYP2D6 and that have a narrow therapeutic index, including certain antidepressants (tricyclic antidepressants [TCAs], such as nortriptyline, amitriptyline, and imipramine), phenothiazines and Type 1C antiarrhythmics (e.g., propafenone, flecainide), should be approached with caution. Plasma TCA concentrations may need to be monitored and the dose of the TCA may need to be reduced if a TCA is co-administered with duloxetine. Because of the risk of serious ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death potentially associated with elevated plasma levels of thioridazine, duloxetine and thioridazine should not be co-administered [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].Other Clinically Important Drug Interactions
Alcohol - Use of duloxetine concomitantly with heavy alcohol intake may be associated with severe liver injury. For this reason, duloxetine delayed-release capsules should not be prescribed for patients with substantial alcohol use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. When duloxetine and ethanol were administered several hours apart so that peak concentrations of each would coincide, duloxetine did not increase the impairment of mental and motor skills caused by alcohol. In the duloxetine clinical trials database, three duloxetine-treated patients had liver injury as manifested by ALT and total bilirubin elevations, with evidence of obstruction. Substantial intercurrent ethanol use was present in each of these cases, and this may have contributed to the abnormalities seen [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. CNS Acting Drugs - Given the primary CNS effects of duloxetine, it should be used with caution when it is taken in combination with or substituted for other centrally acting drugs, including those with a similar mechanism of action [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].5.13 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with SSRIs and SNRIs, including duloxetine. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH). Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Elderly patients may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SSRIs and SNRIs. Also, patients taking diuretics or who are otherwise volume depleted may be at greater risk [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)]. Discontinuation of DRIZALMA Sprinkle should be considered in patients with symptomatic hyponatremia and appropriate medical intervention should be instituted. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which may lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have been included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death.5.14 Use in Patients with Concomitant Illness
Clinical experience with duloxetine delayed-release capsules in patients with concomitant systemic illnesses is limited. There is no information on the effect that alterations in gastric motility may have on the stability of duloxetine delayed-release capsule enteric coating. In extremely acidic conditions, duloxetine, unprotected by the enteric coating, may undergo hydrolysis to form naphthol. Caution is advised in using duloxetine delayed-release capsules in patients with conditions that may slow gastric emptying (e.g., some diabetics). Duloxetine delayed-release capsules have not been systematically evaluated in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable coronary artery disease. Patients with these diagnoses were generally excluded from clinical studies during the product’s premarketing testing. Hepatic Impairment - Avoid use in patients with chronic liver disease or cirrhosis [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), and Use in Specific Populations (8.9)]. Severe Renal Impairment - Avoid use in patients with severe renal impairment, CrCl ≥15 to <30 mL/min . Increased plasma concentration of duloxetine, and especially of its metabolites, occur in patients with end-stage renal disease (requiring dialysis) [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Use in Specific Populations (8.10)]. Glycemic Control in Patients with Diabetes - As observed in DPNP trials, duloxetine delayed-release capsules treatment worsens glycemic control in some patients with diabetes. In three clinical trials of duloxetine delayed-release for the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy, the mean duration of diabetes was approximately 12 years, the mean baseline fasting blood glucose was 176 mg/dL, and the mean baseline hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) was 7.8%. In the 12 week acute treatment phase of these studies, duloxetine delayed-release was associated with a small increase in mean fasting blood glucose as compared to placebo. In the extension phase of these studies, which lasted up to 52 weeks, mean fasting blood glucose increased by 12 mg/dL in the duloxetine delayed-release group and decreased by 11.5 mg/dL in the routine care group. HbA1c increased by 0.5% in the duloxetine delayed-release and by 0.2% in the routine care groups.5.15 Urinary Hesitation and Retention
Duloxetine is in a class of drugs known to affect urethral resistance. If symptoms of urinary hesitation develop during treatment with duloxetine delayed-release capsules, consideration should be given to the possibility that they might be drug-related. In post marketing experience, cases of urinary retention have been observed. In some instances of urinary retention associated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules use, hospitalization and/or catheterization has been needed.6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:- Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Adolescents and Young Adults [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Orthostatic Hypotension, Falls and Syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Serotonin Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Increased Risk of Bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Severe Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Discontinuation Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Activation of Mania/Hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Angle-Closure Glaucoma [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
- Elevated Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Clinically Important Drug Interactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Urinary Hesitation and Retention [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. The stated frequencies of adverse reactions represent the proportion of individuals who experienced, at least once, a treatment-emergent adverse reaction of the type listed. A reaction was considered treatment-emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation. Reactions reported during the studies were not necessarily caused by the therapy, and the frequencies do not reflect investigator impression (assessment) of causality. Adults - The data described below reflect exposure to duloxetine delayed-release capsules in placebo-controlled trials for MDD (N = 3779), GAD (N = 1018), OA (N = 503), CLBP (N = 600), and DPNP (N = 906), and another indication (N = 1294). The population studied was 17 to 89 years of age; 65.7%, 60.8%, 60.6%, 42.9%, and 94.4% female; and 81.8%, 72.6%, 85.3%, 74.0%, and 85.7% Caucasian for MDD, GAD, OA and CLBP, DPNP, and another indication, respectively. Most patients received doses of a total of 60 to 120 mg per day [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The data below do not include results of the trial examining the efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release in patients ≥ 65 years old for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder; however, the adverse reactions observed in this geriatric sample were generally similar to adverse reactions in the overall adult population. Children and Adolescents - The data described below reflect exposure to duloxetine delayed-release capsules in pediatric, 10 week, placebo-controlled trials for MDD (N = 341) and GAD (N = 135). The population studied (N = 476) was 7 to 17 years of age with 42.4% children age 7 to 11 years of age, 50.6% female, and 68.6% white. Patients received 30 to 120 mg per day during placebo-controlled acute treatment studies. Additional data come from the overall total of 822 pediatric patients (age 7 to 17 years of age) with 41.7% children age 7 to 11 years of age and 51.8% female exposed to duloxetine delayed-release capsules in MDD and GAD clinical trials up to 36 weeks in length, in which most patients received 30 to 120 mg per day.Adverse Reactions Reported as Reasons for Discontinuation of Treatment in Adult Placebo-Controlled Trials
Major Depressive Disorder - Approximately 8.4% (319/3779) of the patients who received duloxetine delayed-release capsules in placebo-controlled trials for MDD discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with 4.6% (117/2536) of the patients receiving placebo. Nausea (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 1.1%, placebo 0.4%) was the only common adverse reaction reported as a reason for discontinuation and considered to be drug-related (i.e., discontinuation occurring in at least 1% of the duloxetine delayed-release capsules-treated patients and at a rate of at least twice that of placebo). Generalized Anxiety Disorder - Approximately 13.7% (139/1018) of the patients who received duloxetine delayed-release capsules in placebo-controlled trials for GAD discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with 5.0% (38/767) for placebo. Common adverse reactions reported as a reason for discontinuation and considered to be drug-related (as defined above) included nausea (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 3.3%, placebo 0.4%), and dizziness (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 1.3%, placebo 0.4%). Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain - Approximately 12.9% (117/906) of the patients who received duloxetine delayed-release capsules in placebo-controlled trials for DPNP discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with 5.1% (23/448) for placebo. Common adverse reactions reported as a reason for discontinuation and considered to be drug-related (as defined above) included nausea (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 3.5%, placebo 0.7%), dizziness (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 1.2%, placebo 0.4%), and somnolence (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 1.1%, placebo 0.0%). Chronic Pain due to Osteoarthritis - Approximately 15.7% (79/503) of the patients who received duloxetine delayed-release capsules in 13 week, placebo-controlled trials for chronic pain due to OA discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with 7.3% (37/508) for placebo. Common adverse reactions reported as a reason for discontinuation and considered to be drug-related (as defined above) included nausea (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 2.2%, placebo 1.0%). Chronic Low Back Pain - Approximately 16.5% (99/600) of the patients who received duloxetine delayed-release capsules in 13 week, placebo-controlled trials for CLBP discontinued treatment due to an adverse reaction, compared with 6.3% (28/441) for placebo. Common adverse reactions reported as a reason for discontinuation and considered to be drug-related (as defined above) included nausea (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 3.0%, placebo 0.7%), and somnolence (duloxetine delayed-release capsules 1.0%, placebo 0.0%).Most Common Adverse Reactions (Adults)
Pooled Trials for all Approved Indications - The most commonly observed adverse reactions in duloxetine treated patients (incidence of at least 5% and at least twice the incidence in placebo patients) were nausea, dry mouth, somnolence, constipation, decreased appetite, and hyperhidrosis. Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain - The most commonly observed adverse reactions in duloxetine treated patients (as defined above) were nausea, somnolence, decreased appetite, constipation, hyperhidrosis, and dry mouth. Chronic Pain due to Osteoarthritis - The most commonly observed adverse reactions in duloxetine treated patients (as defined above) were nausea, fatigue, constipation, dry mouth, insomnia, somnolence, and dizziness. Chronic Low Back Pain - The most commonly observed adverse reactions in duloxetine treated patients (as defined above) were nausea, dry mouth, insomnia, somnolence, constipation, dizziness, and fatigue.Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 5% or More Among Duloxetine Delayed-Release Capsules Treated Patients in Adult Placebo-Controlled Trials
Table 2 gives the incidence of adverse reactions in placebo-controlled trials for approved indications that occurred in 5% or more of patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules and with an incidence greater than placebo.Table 2: Adverse Reactions: Incidence of 5% or More and Greater than Placebo in Placebo-Controlled Trials of Approved Indicationsa
| Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Patients Reporting Reaction | |
|---|---|---|
| Duloxetine delayed-release capsules (N = 8100) | Placebo (N = 5655) | |
| Nauseac | 23 | 8 |
| Headache | 14 | 12 |
| Dry mouth | 13 | 5 |
| Somnolencee | 10 | 3 |
| Fatigueb,c | 9 | 5 |
| Insomniad | 9 | 5 |
| Constipationc | 9 | 4 |
| Dizzinessc | 9 | 5 |
| Diarrhea | 9 | 6 |
| Decreased appetitec | 7 | 2 |
| Hyperhidrosisc | 6 | 1 |
| Abdominal painf | 5 | 4 |
Adverse Reactions Occurring at an Incidence of 2% or More Among Duloxetine Delayed-Release Capsules Treated Patients in Adult Placebo-Controlled Trials
Pooled MDD and GAD Trials - Table 3 gives the incidence of adverse reactions in MDD and GAD placebo-controlled trials for approved indications that occurred in 2% or more of patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules and with an incidence greater than placebo.Table 3: Adverse Reactions: Incidence of 2% or More and Greater than Placebo in MDD and GAD Placebo-Controlled Trials a,b
| System Organ Class / Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Patients Reporting Reaction | |
|---|---|---|
| Duloxetine delayed-release capsules (N = 4797) | Placebo (N = 3303) | |
| Cardiac Disorders Palpitations | 2 | 1 |
| Eye Disorders Vision blurred | 3 | 1 |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders Nauseac Dry mouth Constipationc Diarrhea Abdominal paind Vomiting | 23 14 9 9 5 4 | 8 6 4 6 4 2 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatiguee | 9 | 5 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetitec | 6 | 2 |
| Nervous System Disorders Headache Dizzinessc Somnolencef Tremor | 14 9 9 3 | 14 5 3 1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders Insomniag Agitationh Anxiety | 9 4 3 | 5 2 2 |
| Reproductive System and Breast Disorders Erectile dysfunction Ejaculation delayedc Libido decreasedi Orgasm abnormalj | 4 2 3 2 | 1 1 1 <1 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders Yawning | 2 | <1 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Hyperhidrosis | 6 | 2 |
Table 4: Adverse Reactions: Incidence of 2% or More and Greater than Placebo in DPNP, Another Indication, OA, and CLBP Placebo-Controlled Trialsa
| System Organ Class / Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Patients Reporting Reaction | |
|---|---|---|
| Duloxetine delayed-release capsules (N = 3303) | Placebo (N = 2352) | |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders Nausea Dry Mouthb Constipationb Diarrhea Abdominal Painc Vomiting Dyspepsia | 23 11 10 9 5 3 2 | 7 3 3 5 4 2 1 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatigued | 11 | 5 |
| Infections and Infestations Nasopharyngitis Upper Respiratory Tract Infection Influenza | 4 3 2 | 4 3 2 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased Appetiteb | 8 | 1 |
| Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Musculoskeletal Paine Muscle Spasms | 3 2 | 3 2 |
| Nervous System Disorders Headache Somnolenceb,f Dizziness Paraesthesiag Tremorb | 13 11 9 2 2 | 8 3 5 2 <1 |
| Psychiatric Disorders Insomniab,h Agitationi | 10 3 | 5 1 |
| Reproductive System and Breast Disorders Erectile Dysfunctionb Ejaculation Disorderj | 4 2 | <1 <1 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders Cough | 2 | 2 |
| Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Hyperhidrosis | 6 | 1 |
| Vascular Disorders Flushingk Blood pressure increasedl | 3 2 | 1 1 |
Effects on Male and Female Sexual Function in Adults
Changes in sexual desire, sexual performance and sexual satisfaction often occur as manifestations of psychiatric disorders or diabetes, but they may also be a consequence of pharmacologic treatment. Because adverse sexual reactions are presumed to be voluntarily underreported, the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX), a validated measure designed to identify sexual side effects, was used prospectively in 4 MDD placebo-controlled trials. In these trials, as shown in Table 5 below, patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules experienced significantly more sexual dysfunction, as measured by the total score on the ASEX, than did patients treated with placebo. Gender analysis showed that this difference occurred only in males. Males treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules experienced more difficulty with ability to reach orgasm (ASEX Item 4) than males treated with placebo. Females did not experience more sexual dysfunction on duloxetine delayed-release capsules than on placebo as measured by ASEX total score. Negative numbers signify an improvement from a baseline level of dysfunction, which is commonly seen in depressed patients. Physicians should routinely inquire about possible sexual side effects.Table 5: Mean Change in ASEX Scores by Gender in MDD Placebo-Controlled Trials
| ASEX Total (Items 1-5) Item 1 - Sex drive Item 2 - Arousal Item 3 - Ability to achieve erection (men); Lubrication (women) Item 4 - Ease of reaching orgasm Item 5 - Orgasm satisfaction | Male Patientsa | Female Patientsa | ||
| Duloxetine delayed- release capsules (n = 175) | Placebo (n = 83) | Duloxetine delayed-release capsules (n = 241) | Placebo (n = 126) | |
| 0.56b -0.07 0.01 0.03 0.40c 0.09 | -1.07 -0.12 -0.26 -0.25 -0.24 -0.13 | -1.15 -0.32 -0.21 -0.17 -0.09 -0.11 | -1.07 -0.24 -0.18 -0.18 -0.13 -0.17 | |
Vital Sign Changes in Adults
In placebo-controlled clinical trials across approved indications for change from baseline to endpoint, duloxetine delayed-release capsules treatment was associated with mean increases of 0.23 mm Hg in systolic blood pressure and 0.73 mm Hg in diastolic blood pressure compared to mean decreases of 1.09 mm Hg systolic and 0.55 mm Hg diastolic in placebo-treated patients. There was no significant difference in the frequency of sustained (3 consecutive visits) elevated blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.11)]. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules treatment, for up to 26 weeks in placebo-controlled trials across approved indications, typically caused a small increase in heart rate for change from baseline to endpoint compared to placebo of up to 1.37 beats per minute (increase of 1.20 beats per minute in duloxetine delayed-release capsules-treated patients, decrease of 0.17 beats per minute in placebo-treated patients).Laboratory Changes in Adults
Duloxetine delayed-release capsules treatment in placebo-controlled clinical trials across approved indications, was associated with small mean increases from baseline to endpoint in ALT, AST, CPK, and alkaline phosphatase; infrequent, modest, transient, abnormal values were observed for these analytes in duloxetine delayed-release capsules-treated patients when compared with placebo-treated patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. High bicarbonate, cholesterol, and abnormal (high or low) potassium, were observed more frequently in duloxetine delayed-release capsules treated patients compared to placebo.Electrocardiogram Changes in Adults
The effect of duloxetine delayed-release capsules 160 mg and 200 mg administered twice daily to steady state was evaluated in a randomized, double-blinded, two-way crossover study in 117 healthy female subjects. No QT interval prolongation was detected. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules appears to be associated with concentration-dependent but not clinically meaningful QT shortening.Other Adverse Reactions Observed During the Premarketing and Postmarketing Clinical Trial Evaluation of Duloxetine Delayed-Release Capsules in Adults
Following is a list of adverse reactions reported by patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules in clinical trials. In clinical trials of all indications, 34,756 patients were treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Of these, 26.9% (9337) took duloxetine delayed-release capsules for at least 6 months, and 12.4% (4317) for at least one year. The following listing is not intended to include reactions (1) already listed in previous tables or elsewhere in labeling, (2) for which a drug cause was remote, (3) which were so general as to be uninformative, (4) which were not considered to have significant clinical implications, or (5) which occurred at a rate equal to or less than placebo. Reactions are categorized by body system according to the following definitions: frequent adverse reactions are those occurring in at least 1/100 patients; infrequent adverse reactions are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1000 patients; rare reactions are those occurring in fewer than 1/1000 patients.Cardiac Disorders - Frequent: palpitations; Infrequent: myocardial infarction, tachycardia, and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Ear and Labyrinth Disorders - Frequent: vertigo; Infrequent: ear pain and tinnitus.
Endocrine Disorders - Infrequent: hypothyroidism.
Eye Disorders - Frequent: vision blurred; Infrequent: diplopia, dry eye, and visual impairment.
Gastrointestinal Disorders - Frequent: flatulence; Infrequent: dysphagia, eructation, gastritis, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, halitosis, and stomatitis; Rare: gastric ulcer.
General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions - Frequent: chills/rigors; Infrequent: falls, feeling abnormal, feeling hot and/or cold, malaise, and thirst; Rare: gait disturbance.
Infections and Infestations - Infrequent: gastroenteritis and laryngitis.
Investigations - Frequent: weight increased, weight decreased; Infrequent: blood cholesterol increased.
Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders - Infrequent: dehydration and hyperlipidemia; Rare: dyslipidemia.
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders - Frequent: musculoskeletal pain; Infrequent: muscle tightness and muscle twitching.
Nervous System Disorders - Frequent: dysgeusia, lethargy, and paraesthesia/hypoesthesia; Infrequent: disturbance in attention, dyskinesia, myoclonus, and poor quality sleep; Rare: dysarthria.
Psychiatric Disorders - Frequent: abnormal dreams and sleep disorder; Infrequent: apathy, bruxism, disorientation/confusional state, irritability, mood swings, and suicide attempt; Rare: completed suicide.
Renal and Urinary Disorders - Frequent: urinary frequency; Infrequent: dysuria, micturition urgency, nocturia, polyuria, and urine odor abnormal.
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders - Frequent: anorgasmia/orgasm abnormal; Infrequent: menopausal symptoms, sexual dysfunction, and testicular pain; Rare: menstrual disorder.
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders - Frequent: yawning, oropharyngeal pain; Infrequent: throat tightness.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders - Frequent: pruritus; Infrequent: cold sweat, dermatitis contact, erythema, increased tendency to bruise, night sweats, and photosensitivity reaction; Rare: ecchymosis.
Vascular Disorders - Frequent: hot flush; Infrequent: flushing, orthostatic hypotension, and peripheral coldness.
Adverse Reactions Observed in Children and Adolescent Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
The adverse drug reaction profile observed in pediatric clinical trials (children and adolescents) was consistent with the adverse drug reaction profile observed in adult clinical trials. The specific adverse drug reactions observed in adult patients can be expected to be observed in pediatric patients (children and adolescents) [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The most common (≥5% and twice placebo) adverse reactions observed in pediatric clinical trials include: nausea, diarrhea, decreased weight, and dizziness. Table 6 provides the incidence of adverse reactions in MDD and GAD pediatric placebo- controlled trials that occurred in greater than 2% of patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules and with an incidence greater than placebo.Table 6: Adverse Reactions: Incidence of 2% or More and Greater than Placebo in three 10 week Pediatric Placebo-Controlled Trialsa
| System Organ Class/Adverse Reaction | Percentage of Pediatric Patients Reporting Reaction | |
|---|---|---|
| Duloxetine delayed-release capsules (N = 476) | Placebo (N = 362) | |
| Gastrointestinal Disorders Nausea Abdominal Painb Vomiting Diarrhea Dry Mouth | 18 13 9 6 2 | 8 10 4 3 1 |
| General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Fatiguec | 7 | 5 |
| Investigations Decreased Weightd | 14 | 6 |
| Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased Appetite | 10 | 5 |
| Nervous System Disorders Headache Somnolencee Dizziness | 18 11 8 | 13 6 4 |
| Psychiatric Disorders Insomniaf | 7 | 4 |
| Respiratory, Thoracic, and Mediastinal Disorders Oropharyngeal Pain Cough | 4 3 | 2 1 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Adverse reactions reported since market introduction that were temporally related to duloxetine delayed-release capsules therapy and not mentioned elsewhere in labeling include: acute pancreatitis, anaphylactic reaction, aggression and anger (particularly early in treatment or after treatment discontinuation), angioneurotic edema, angle-closure glaucoma, colitis (microscopic or unspecified), cutaneous vasculitis (sometimes associated with systemic involvement), extrapyramidal disorder, galactorrhea, gynecological bleeding, hallucinations, hyperglycemia, hyperprolactinemia, hypersensitivity, hypertensive crisis, muscle spasm, rash, restless legs syndrome, seizures upon treatment discontinuation, supraventricular arrhythmia, tinnitus (upon treatment discontinuation), trismus, and urticaria.7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions with DRIZALMA Sprinkle
Table 7: Clinically Important Drug Interactions
| Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of SSRIs and SNRIs including duloxetine with MAOIs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention |
|
| Examples | Selegiline, tranylcypromine, isocarboxazid, phenelzine, linezolid, intravenous methylene blue |
| Serotonergic Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with other serotonergic drugs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
| Intervention |
|
| Examples | Triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, other SNRIs or SSRIs, and St. John’s Wort |
| Inhibitors of CYP1A2 | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with CYP1A2 inhibitors increases AUC, Cmax, t1/2 of duloxetine. |
| Intervention | Avoid concomitant use of duloxetine delayed-release capsules with potent CYP1A2 inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | Fluvoxamine, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, enoxacin |
| Dual Inhibition of CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant administration of duloxetine with potent CYP1A2 inhibitors to CYP2D6 poor metabolizers results in increased AUC and Cmax of duloxetine. |
| Intervention | Avoid co-administration of duloxetine delayed-release capsules and potent CYP1A2 inhibitors to CYP2D6 poor metabolizers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | Fluvoxamine, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, enoxacin |
| Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with an antiplatelet or anticoagulant drug may potentiate the risk of bleeding. |
| Intervention | Closely monitor for bleeding for patients receiving an antiplatelet or anticoagulant drug when duloxetine is initiated or discontinued [Warnings and Precaution (5.5)]. |
| Examples | NSAIDs, aspirin, warfarin |
| Inhibitors of CYP2D6 | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with CYP2D6 inhibitors increase AUC of duloxetine. Greater degrees of inhibition are expected with higher doses of CYP2D6 inhibitors. |
| Intervention | Exercise caution when co-administering duloxetine delayed-release capsules and potent CYP2D6 inhibitors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | Paroxetine, fluoxetine, quinidine |
| Drugs Metabolized by CYP2D6 | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine increases AUC of a drug primarily metabolized by CYP2D6 which may increase the risk of toxicity of the CYP2D6 substrate drug. |
| Intervention | Monitor plasma concentrations of CYP2D6 substrate and reduce dosage of CYP2D6 substrate drug if necessary [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | TCAs (nortriptyline, amitriptyline, imipramine, desipramine); phenothiazines (thioridazine); Type 1C antiarrhythmics (propafenone, flecainide) |
| Drugs that Affect Gastric Acidity | |
| Clinical Impact | In patients with conditions that may slow gastric emptying (e.g., some diabetics) and drugs that raise the gastrointestinal pH may lead to earlier the release of duloxetine. |
| Intervention | Use with caution [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | Aluminum-and magnesium-containing antacids, famotidine, proton pump inhibitors |
| Drugs Metabolized by CYP1A2 | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with CYP1A2 substrates may increase the AUC of CYP1A2 substrate. |
| Intervention | Use with caution [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | Theophylline, caffeine |
| CNS Drugs | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with other centrally acting drugs may increase the CNS effects of duloxetine. |
| Intervention | Use with caution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]. |
| Examples | Centrally acting CNS drugs |
| Drugs Highly Bound to Plasma Protein | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine with highly protein bound drugs may cause increased free concentrations of the other drug, potentially resulting in adverse reactions. |
| Intervention | Use with caution [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
| Examples | Highly plasma protein binding drugs |
| Alcohol | |
| Clinical Impact | Concomitant use of duloxetine and alcohol may cause liver injury or aggravate pre-existing liver disease. |
| Intervention | Avoid use patients with chronic liver disease or heavy alcohol use [see Dosage and Administration (2.7), Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.12)]. |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Exposure Registry
There is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy. Healthcare providers are encouraged to register patients by calling the National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants at 1-844-405-6185 or visiting online at https://womensmentalhealth.org/clinical-and-research-programs/pregnancyregistry/antidepressants/Risk Summary
Data from published observational studies with duloxetine use in pregnant women have not identified a clear drug-associated risk of major birth defects or adverse developmental outcomes. There are risks associated with untreated depression in pregnancy and with exposure to SNRIs and SSRIs, including duloxetine delayed-release capsules, during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). In rats and rabbits treated with duloxetine during the period of organogenesis, fetal weights were decreased but there was no evidence of developmental effects at doses up to 3 and 6 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 120 mg/day given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis. When duloxetine was administered orally to pregnant rats throughout gestation and lactation, pup weights at birth and pup survival to 1 day postpartum were decreased at a dose 2 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis. At this dose, pup behaviors consistent with increased reactivity, such as increased startle response to noise and decreased habituation of locomotor activity were observed. Post-weaning growth was not adversely affected. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules should be used in pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. The estimated of background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk - Women who discontinued antidepressants during pregnancy are more likely to experience a relapse of major depression than women who continued antidepressants. This finding is from a prospective, longitudinal study that followed 201 pregnant women with a history of major depressive disorder who were euthymic and taking antidepressants at the beginning of pregnancy. Consider the risk of untreated depression when discontinuing or changing treatment with antidepressant medication during pregnancy and the postpartum. Fetal/Neonatal Adverse Reaction - Neonates exposed to duloxetine and other SNRIs or SSRIs late in the third trimester have developed complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support, and tube feeding. Such complications can arise immediately upon delivery. Reported clinical findings have included respiratory distress, cyanosis, apnea, seizures, temperature instability, feeding difficulty, vomiting, hypoglycemia, hypotonia, hypertonia, hyperreflexia, tremor, jitteriness, irritability, and constant crying. These findings are consistent with either a direct toxic effect of the SNRIs or SSRIs, or possibly, a drug discontinuation syndrome. It should be noted that, in some cases, the clinical picture is consistent with serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].Data
Animal Data - In animal reproduction studies, duloxetine has been shown to have adverse effects on embryo/fetal and postnatal development. When duloxetine was administered orally to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis, there was no evidence of malformations or developmental variations at doses up to 45 mg/kg/day (3 and 6 times, respectively, the MRHD of 120 mg/day given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis. However, fetal weights were decreased at this dose, with a no-effect dose of 10 mg/kg/day (approximately equal to the MRHD in rats and 2 times the MRHD in rabbits). When duloxetine was administered orally to pregnant rats throughout gestation and lactation, the survival of pups to 1 day postpartum and pup body weights at birth and during the lactation period were decreased at a dose of 30 mg/kg/day (2 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis); the no-effect dose was 10 mg/kg/day. Furthermore, behaviors consistent with increased reactivity, such as increased startle response to noise and decreased habituation of locomotor activity, were observed in pups following maternal exposure to 30 mg/kg/day. Post-weaning growth and reproductive performance of the progeny were not affected adversely by maternal duloxetine treatment.8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary Data from the published literature report the presence of duloxetine in human milk (see Data). There are no data on the effect of duloxetine on the breastfed infant or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for duloxetine delayed-release capsules and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from the duloxetine delayed-release capsules or from the underlying maternal condition. Data The disposition of duloxetine was studied in 6 lactating women who were at least 12 weeks postpartum and had elected to wean their infants. The women were given 40 mg of duloxetine delayed-release capsules twice daily for 3.5 days. The peak concentration measured in breast milk occurred at a median of 3 hours after the dose. The amount of duloxetine in breast milk was approximately 7 mcg/day while on that dose; the estimated daily infant dose was approximately 2 mcg/kg/day, which is less than 1% of the maternal dose. The presence of duloxetine metabolites in breast milk was not examined.8.4 Pediatric Use
Generalized Anxiety Disorder - In pediatric patients aged 7 to 17 years, efficacy was demonstrated in one 10 week, placebo-controlled trial. The study included 272 pediatric patients with GAD of which 47% were 7 to 11 years of age. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules demonstrated superiority over placebo as measured by greater improvement in the Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale (PARS) for GAD severity score [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. The safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 7 years of age have not been established. Major Depressive Disorder - Efficacy was not demonstrated in two 10 week, placebo-controlled trials with 800 pediatric patients with MDD, age 7 to 17. Neither duloxetine delayed-release capsules nor an active control (indicated for treatment of pediatric depression) was superior to placebo. The safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients less than 7 years of age have not been established. The most frequently observed adverse reactions in the clinical trials included nausea, headache, decreased weight, and abdominal pain. Decreased appetite and weight loss have been observed in association with the use of SSRIs and SNRIs. Perform regular monitoring of weight and growth in children and adolescents treated with an SNRI such as duloxetine [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Use of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Animal Data - Duloxetine administration to young rats from post-natal day 21 (weaning) through post-natal day 90 (adult) resulted in decreased body weights that persisted into adulthood, but recovered when drug treatment was discontinued; slightly delayed (~1.5 days) sexual maturation in females, without any effect on fertility; and a delay in learning a complex task in adulthood, which was not observed after drug treatment was discontinued. These effects were observed at the high dose of 45 mg/kg/day (2 times the MRHD, for a child); the no-effect-level was 20 mg/kg/day (≈1 times the MRHD, for a child).8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 2,418 patients in premarketing clinical studies of duloxetine delayed-release capsules for MDD, 5.9% (143) were 65 years of age or over. Of the 1041 patients in CLBP premarketing studies, 21.2% (221) were 65 years of age or over. Of the 487 patients in OA premarketing studies, 40.5% (197) were 65 years of age or over. Of the 1,074 patients in the DPNP premarketing studies, 33% (357) were 65 years of age or over. In the MDD, GAD, DPNP, OA, and CLBP studies, no overall differences in safety or effectiveness were generally observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. SSRIs and SNRIs, including duloxetine have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse event [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. In an analysis of data from all placebo-controlled-trials, patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules reported a higher rate of falls compared to patients treated with placebo. The increased risk appears to be proportional to a patient’s underlying risk for falls. Underlying risk appears to increase steadily with age. As elderly patients tend to have a higher prevalence of risk factors for falls such as medications, medical comorbidities and gait disturbances, the impact of increasing age by itself on falls during treatment with duloxetine delayed-release capsules is unclear. Falls with serious consequences including bone fractures and hospitalizations have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The pharmacokinetics of duloxetine after a single dose of 40 mg were compared in healthy elderly females (65 to 77 years) and healthy middle-age females (32 to 50 years). There was no difference in the Cmax, but the AUC of duloxetine was somewhat (about 25%) higher and the half-life about 4 hours longer in the elderly females. Population pharmacokinetic analyses suggest that the typical values for clearance decrease by approximately 1% for each year of age between 25 to 75 years of age; but age as a predictive factor only accounts for a small percentage of between-patient variability. Dosage adjustment based on the age of the patient is not necessary.8.6 Gender
Duloxetine’s half-life is similar in men and women. Dosage adjustment based on gender is not necessary.8.7 Smoking Status
Duloxetine bioavailability (AUC) appears to be reduced by about one-third in smokers. Dosage modifications are not recommended for smokers.8.8 Race
No specific pharmacokinetic study was conducted to investigate the effects of race.8.9 Hepatic Impairment
Avoid use in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A), moderate (Child-Pugh B), or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]. Patients with clinically evident hepatic impairment have decreased duloxetine metabolism and elimination. After a single 20 mg dose of duloxetine delayed-release capsules, 6 cirrhotic patients with moderate liver impairment (Child-Pugh Class B) had a mean plasma duloxetine clearance about 15% that of age- and gender-matched healthy subjects, with a 5 fold increase in mean exposure (AUC). Although Cmax was similar to normals in the cirrhotic patients, the half-life was about 3 times longer.8.10 Severe Renal Impairment
Avoid use in patients with severe renal impairment (CrCl ≥15 to <30 mL/min) [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]. Limited data are available on the effects of duloxetine in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD). After a single 60 mg dose of duloxetine, Cmax and AUC values were approximately 100% greater in patients with end-stage renal disease receiving chronic intermittent hemodialysis than in subjects with normal renal function. The elimination half-life, however, was similar in both groups. The AUCs of the major circulating metabolites, 4-hydroxy duloxetine glucuronide and 5-hydroxy, 6-methoxy duloxetine sulfate, largely excreted in urine, were approximately 7 to 9 fold higher and would be expected to increase further with multiple dosing. Population PK analyses suggest that mild to moderate degrees of renal impairment (estimated CrCl 30 to 80 mL/min) have no significant effect on duloxetine apparent clearance [see Dosage and Administration (2.7) and Warnings and Precautions (5.14)].9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.2 Abuse
In animal studies, duloxetine did not demonstrate barbiturate-like (depressant) abuse potential. While duloxetine delayed-release capsules have not been systematically studied in humans for its potential for abuse, there was no indication of drug-seeking behavior in the clinical trials. However, it is not possible to predict on the basis of premarketing experience the extent to which a CNS active drug will be misused, diverted, and/or abused once marketed. Consequently, physicians should carefully evaluate patients for a history of drug abuse and follow such patients closely, observing them for signs of misuse or abuse of duloxetine delayed-release capsules (e.g., development of tolerance, incrementation of dose, drug-seeking behavior).9.3 Dependence
In drug dependence studies, duloxetine did not demonstrate dependence-producing potential in rats.10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
In postmarketing experience, fatal outcomes have been reported for acute overdoses, primarily with mixed overdoses, but also with duloxetine only, at doses as low as 1000 mg. Signs and symptoms of overdose (duloxetine alone or with mixed drugs) included somnolence, coma, serotonin syndrome, seizures, syncope, tachycardia, hypotension, hypertension, and vomiting.10.2 Management of Overdose
There is no specific antidote to duloxetine, but if serotonin syndrome ensues, specific treatment (such as with cyproheptadine and/or temperature control) may be considered. In case of acute overdose, treatment should consist of those general measures employed in the management of overdose with any drug. An adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation should be assured, and cardiac rhythm and vital signs should be monitored. Induction of emesis is not recommended. Gastric lavage with a large-bore orogastric tube with appropriate airway protection, if needed, may be indicated if performed soon after ingestion or in symptomatic patients. Activated charcoal may be useful in limiting absorption of duloxetine from the gastrointestinal tract. Administration of activated charcoal has been shown to decrease AUC and Cmax by an average of one-third, although some subjects had a limited effect of activated charcoal. Due to the large volume of distribution of this drug, forced diuresis, dialysis, hemoperfusion, and exchange transfusion are unlikely to be beneficial. In managing overdose, the possibility of multiple drug involvement should be considered. A specific caution involves patients who are taking or have recently taken duloxetine delayed-release capsules and might ingest excessive quantities of a TCA. In such a case, decreased clearance of the parent tricyclic and/or its active metabolite may increase the possibility of clinically significant sequelae and extend the time needed for close medical observation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4) and Drug Interactions (7)]. In case of an overdose, consult a Certified Poison Control Center (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org) for up-to-date guidance and advice.11 DESCRIPTION
Duloxetine hydrochloride is a selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). The chemical name of duloxetine hydrochloride is (+)-(S)-N-methyl-γ-(1-naphthyloxy)-2-thiophenepropylamine hydrochloride. The molecular formula is C18H19NOS•HCl, which corresponds to a molecular weight of 333.88. The structural formula is:
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Although the exact mechanisms of the antidepressant, central pain inhibitory and anxiolytic actions of duloxetine in humans are unknown, these actions are believed to be related to its potentiation of serotonergic and noradrenergic activity in the CNS.12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Preclinical studies have shown that duloxetine is a potent inhibitor of neuronal serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake and a less potent inhibitor of dopamine reuptake. Duloxetine has no significant affinity for dopaminergic, adrenergic, cholinergic, histaminergic, opioid, glutamate, and GABA receptors in vitro. Duloxetine does not inhibit monoamine oxidase (MAO). Duloxetine is in a class of drugs known to affect urethral resistance. If symptoms of urinary hesitation develop during treatment with duloxetine delayed-release capsules, consideration should be given to the possibility that they might be drug-related.12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Duloxetine hydrochloride pharmacokinetics are dose proportional over the therapeutic range. Steady-state plasma concentrations are typically achieved after 3 days of dosing.Absorption
Orally administered duloxetine hydrochloride is well absorbed. Peak plasma concentration of duloxetine is attained at 5 hours following administration of duloxetine delayed-release capsules. There is a 3 hour delay in absorption and a one- third increase in apparent clearance of duloxetine after an evening dose as compared to a morning dose. Effect of food Compared to fasted state administration, high-fat, high-calorie meal (containing approximately 150 kcal from protein, 250 kcal from carbohydrates and 500 kcal from fat) did not have a significant effect on Cmax and AUC of duloxetine hydrochloride. However, Tmax of duloxetine hydrochloride delayed by approximately 1.7 hours with the administration of high-fat, high-calorie meal. Duloxetine delayed-release capsules administered under fasting conditions to healthy adults by sprinkling the entire contents on one-tablespoon (15 mL) of applesauce did not significantly affect Tmax, Cmax, and AUC of duloxetine.Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution averages about 1640 L. Duloxetine is highly bound (>90%) to proteins in human plasma, binding primarily to albumin and α1-acid glycoprotein. The interaction between duloxetine and other highly protein bound drugs has not been fully evaluated. Plasma protein binding of duloxetine is not affected by renal or hepatic impairment.Elimination
Only trace (<1% of the dose) amounts of unchanged duloxetine are present in the urine. Most (about 70%) of the duloxetine dose appears in the urine as metabolites of duloxetine; about 20% is excreted in the feces. Mean terminal half-life was 12.4 hours (range 7.8 to 22.2 hour) in subjects receiving a single dose duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Metabolism Biotransformation and disposition of duloxetine in humans have been determined following oral administration of 14C-labeled duloxetine. Duloxetine comprises about 3% of the total radiolabeled material in the plasma, indicating that it undergoes extensive metabolism to numerous metabolites. The major biotransformation pathways for duloxetine involve oxidation of the naphthyl ring followed by conjugation and further oxidation. Both CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 catalyze the oxidation of the naphthyl ring in vitro. Metabolites found in plasma include 4-hydroxy duloxetine glucuronide and 5-hydroxy, 6-methoxy duloxetine sulfate. Duloxetine undergoes extensive metabolism, but the major circulating metabolites have not been shown to contribute significantly to the pharmacologic activity of duloxetine.Specific Populations
Pediatric Patients Children and Adolescents (ages 7 to 17 years) - Duloxetine steady-state plasma concentration was comparable in children (7 to 12 years of age), adolescents (13 to 17 years of age) and adults. The average steady-state duloxetine concentration was approximately 30% lower in the pediatric population (children and adolescents) relative to the adults. The model-predicted duloxetine steady state plasma concentrations in children and adolescents were mostly within the concentration range observed in adult patients and did not exceed the concentration range in adults.Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies Effect of other drugs on duloxetine Fluvoxamine When duloxetine 60 mg was co-administered with fluvoxamine 100 mg, a potent CYP1A2 inhibitor, to male subjects (n = 14) duloxetine AUC was increased approximately 6 fold, the Cmax was increased about 2.5 fold, and duloxetine t1/2 was increased approximately 3 fold [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Fluvoxamine in CYP2D6 poor metabolizer subjects Concomitant administration of duloxetine 40 mg twice daily with fluvoxamine 100 mg, a potent CYP1A2 inhibitor, to CYP2D6 poor metabolizer subjects (n = 14) resulted in a 6 fold increase in duloxetine AUC and Cmax [see Dosage and Administration (2.6) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Paroxetine Concomitant use of duloxetine (40 mg once daily) with paroxetine (20 mg once daily), a strong CYP2D6 inhibitor, increased the concentration of duloxetine AUC by about 60%, and greater degrees of inhibition are expected with higher doses of paroxetine [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Lorazepam Under steady-state conditions for duloxetine (60 mg Q 12 hours) and lorazepam (2 mg Q 12 hours), the pharmacokinetics of duloxetine were not affected by co-administration. Temazepam Under steady-state conditions for duloxetine (20 mg qhs) and temazepam (30 mg qhs), the pharmacokinetics of duloxetine were not affected by co-administration. Drugs that Affect Gastric Acidity Co-administration of duloxetine delayed-release capsules with aluminum- and magnesium-containing antacids (51 mEq) or duloxetine delayed-release capsules with famotidine, had no significant effect on the rate or extent of duloxetine absorption after administration of a 40 mg oral dose [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Effect of duloxetine on other drugs Theophylline In two clinical studies the average (90% confidence interval) increase in theophylline (a CYP1A2 substrate) AUC was 7% (1% to 15%) and 20% (13% to 27%) when co-administered with duloxetine (60 mg twice daily) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Desipramine When duloxetine was administered (at a dose of 60 mg twice daily) in conjunction with a single 50 mg dose of desipramine, a CYP2D6 substrate, the AUC of desipramine increased 3 fold [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Warfarin Under steady-state condition for warfarin (2 to 9 mg once daily) and duloxetine (60 or 120 mg once daily), the total warfarin (protein bound plus free drug) pharmacokinetics (AUCτ,ss, Cmax,ss or tmax,ss) for both R- and S-warfarin (a CYP2C9 substrate) were not altered by duloxetine [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. In vitro StudiesResults of in vitro studies demonstrate that duloxetine does not inhibit activity of drugs metabolized by CYP3A (e.g., oral contraceptives and other steroidal agents) and drugs metabolized by CYP2C19.
Alcohol An in vitro study showed significant increases of duloxetine hydrochloride release from DRIZALMA Sprinkle at 2 hours to approximately 86% and 56% of the drug release in the presence of 40% and 20% alcohol, respectively. Effect of 5% alcohol on drug release was not observed at 2 hours. There is no in vivo study conducted for the effect of alcohol on drug exposure.13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis - Duloxetine was administered in the diet to mice and rats for 2 years. In female mice receiving duloxetine at 140 mg/kg/day (3 times the MRHD of 120 mg/day given to children on a mg/m2 basis), there was an increased incidence of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas. The no-effect dose was 50 mg/kg/day (1 times the MRHD given to children). Tumor incidence was not increased in male mice receiving duloxetine at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (2 times the MRHD given to children). In rats, dietary doses of duloxetine up to 27 mg/kg/day in females (1 times the MRHD given to children) and up to 36 mg/kg/day in males (1.4 times the MRHD given to children) did not increase the incidence of tumors. Mutagenesis - Duloxetine was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) and was not clastogenic in an in vivo chromosomal aberration test in mouse bone marrow cells. Additionally, duloxetine was not genotoxic in an in vitro mammalian forward gene mutation assay in mouse lymphoma cells or in an in vitro unscheduled DNA synthesis (UDS) assay in primary rat hepatocytes, and did not induce sister chromatid exchange in Chinese hamster bone marrow in vivo. Impairment of Fertility - Duloxetine administered orally to either male or female rats prior to and throughout mating at doses up to 45 mg/kg/day (3 times the MRHD given to adolescents on a mg/m2 basis) did not alter mating or fertility.14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules has been established in the following adequate and well-controlled trials:- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): 4 short-term and 1 maintenance trial in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): 3 short-term trials in adults, 1 maintenance trial in adults, and 1 short-term trial in children and adolescents [see Clinical Studies (14.2)].
- Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain (DPNP): Two 12 week trials in adults [see Clinical Studies (14.3)].
- Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain: Two 12 to 13 week trials in adult patients with chronic low back pain (CLBP) and one 13 week trial in adult patients with chronic pain due to osteoarthritis [see Clinical Studies (14.4)].
14.1 Major Depressive Disorder
The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules as a treatment for depression was established in 4 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose studies in adult outpatients (18 to 83 years) meeting DSM-IV criteria for major depression. In 2 studies, patients were randomized to duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg once daily (N = 123 and N = 128, respectively) or placebo (N = 122 and N = 139, respectively) for 9 weeks; in the third study, patients were randomized to duloxetine delayed-release capsules 20 or 40 mg twice daily (N = 86 and N = 91, respectively) or placebo (N = 89) for 8 weeks; in the fourth study, patients were randomized to duloxetine delayed-release capsules 40 or 60 mg twice daily (N = 95 and N = 93, respectively) or placebo (N = 93) for 8 weeks. There is no evidence that doses greater than 60 mg/day confer additional benefits. In all 4 studies, duloxetine delayed-release capsules demonstrated superiority over placebo as measured by improvement in the 17-item Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAMD-17) total score (Studies 1-4 in Table 8). In all of these clinical studies, analyses of the relationship between treatment outcome and age, gender, and race did not suggest any differential responsiveness on the basis of these patient characteristics.Table 8: Summary of the Primary Efficacy Results for Studies in Major Depressive Disorder
| Study Number | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure: HAMD-17 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Placebo-subtracted Differencea (95% CI) | ||
| Study 1 | Duloxetine delayed-release (60 mg/day)b Placebo | 21.5 (4.10)
21.1 (3.71) | -10.9 (0.70) -6.1 (0.69) | -4.9 (-6.8, -2.9) - |
| Study 2 | Duloxetine delayed-release (60 mg/day)b Placebo | 20.3 (3.32)
20.5 (3.42) | -10.5 (0.71) -8.3 (0.67) | -2.2 (-4.0, -0.3) - |
| Study 3 | Duloxetine delayed-release (20 mg BID)b Duloxetine delayed-release (40 mg BID)b Placebo | 18.6 (5.85)
18.1 (4.52)
17.2 (5.11) | -7.4 (0.80) -8.6 (0.81) -5.0 (0.81) | -2.4 (-4.7, -0.2) -3.6 (-5.9, -1.4) -- |
| Study 4 | Duloxetine delayed-release (40 mg BID)b Duloxetine delayed-release (60 mg BID)b Placebo | 19.9 (3.54)
20.2 (3.41)
19.9 (3.58) | -11.0 (0.49) -12.1 (0.49) -8.8 (0.50) | -2.2 (-3.6, -0.9) -3.3 (-4.7, -1.9) -- |
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier Estimation of Cumulative Proportion of Patients with Relapse (MDD Study 5)
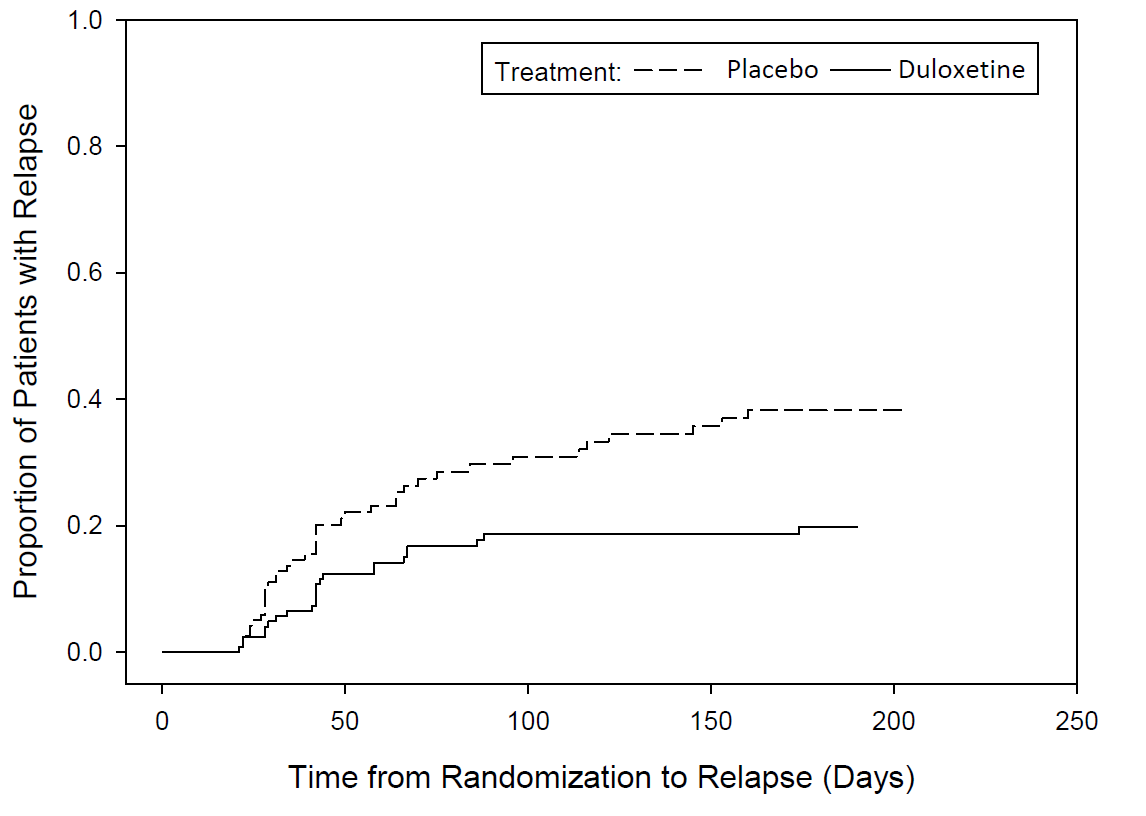
14.2 Generalized Anxiety Disorder
The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) was established in 1 fixed-dose randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial and 2 flexible-dose randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in adult outpatients between 18 and 83 years of age meeting the DSM-IV criteria for GAD. In 1 flexible-dose study and in the fixed-dose study, the starting dose was 60 mg once daily where down titration to 30 mg once daily was allowed for tolerability reasons before increasing it to 60 mg once daily. Fifteen percent of patients were down titrated. One flexible-dose study had a starting dose of 30 mg once daily for 1 week before increasing it to 60 mg once daily. The 2 flexible-dose studies involved dose titration with duloxetine delayed-release capsules doses ranging from 60 mg once daily to 120 mg once daily (N = 168 and N = 162) compared to placebo (N = 159 and N = 161) over a 10 week treatment period. The mean dose for completers at endpoint in the flexible-dose studies was 104.75 mg/day. The fixed-dose study evaluated duloxetine delayed-release capsules doses of 60 mg once daily (N = 168) and 120 mg once daily (N = 170) compared to placebo (N = 175) over a 9 week treatment period. While a 120 mg/day dose was shown to be effective, there is no evidence that doses greater than 60 mg/day confer additional benefit. In all 3 studies, duloxetine delayed-release capsules demonstrated superiority over placebo as measured by greater improvement in the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM-A) total score (Studies 1-3 in Table 9) and by the Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS) global functional impairment score. The SDS is a composite measurement of the extent emotional symptoms disrupt patient functioning in 3 life domains: work/school, social life/leisure activities, and family life/home responsibilities. In another study, 887 patients meeting DSM-IV-TR criteria for GAD received duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg to 120 mg once daily during an initial 26 week open-label treatment phase. Four hundred and twenty-nine patients who responded to open-label treatment (defined as meeting the following criteria at weeks 24 and 26: a decrease from baseline HAM-A total score by at least 50% to a score no higher than 11, and a Clinical Global Impressions of Improvement [CGI-Improvement] score of 1 or 2) were randomly assigned to continuation of duloxetine delayed-release capsules at the same dose (N = 216) or to placebo (N = 213) and were observed for relapse. Of the patients randomized, 73% had been in a responder status for at least 10 weeks. Relapse was defined as an increase in CGI-Severity score at least 2 points to a score ≥4 and a MINI (Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview) diagnosis of GAD (excluding duration), or discontinuation due to lack of efficacy. Patients taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules experienced a statistically significantly longer time to relapse of GAD than did patients taking placebo (Study 4 in Figure 2). Subgroup analyses did not indicate that there were any differences in treatment outcomes as a function of age or gender. The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in the treatment of patients ≥65 years of age with generalized anxiety disorder was established in one 10 week flexible-dose, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in adults ≥65 years of age meeting the DSM-IV criteria for GAD. In this study, the starting dose was 30 mg once daily for 2 weeks before further dose increases in 30 mg increments at treatment weeks 2, 4, and 7 up to 120 mg once daily were allowed based on investigator judgment of clinical response and tolerability. The mean dose for patients completing the 10 week acute treatment phase was 50.95 mg. Patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules (N = 151) demonstrated significantly greater improvement compared with placebo (N = 140) on mean change from baseline to endpoint as measured by the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale total score (Study 5 in Table 9). The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in the treatment of pediatric patients 7 to 17 years of age with generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) was established in 1 flexible-dose randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in pediatric outpatients with GAD (based on DSM-IV criteria). In this study, the starting dose was 30 mg once daily for 2 weeks. Further dose increases in 30 mg increments up to 120 mg once daily were allowed based on investigator judgment of clinical response and tolerability. The mean dose for patients completing the 10 week treatment phase was 57.6 mg/day. In this study, duloxetine delayed-release capsules (N = 135) demonstrated superiority over placebo (N = 137) from baseline to endpoint as measured by greater improvement in the Pediatric Anxiety Rating Scale (PARS) for GAD severity score (Study 6 in Table 9).Table 9: Summary of the Primary Efficacy Results for Studies in General Anxiety Disorder
| Study Number | Treatment Group | Primary Efficacy Measure | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Baseline Score (SD) | LS Mean Change from Baseline (SE) | Placebo-subtracted Differencea (95% CI) | ||
| Study 1 (HAM-A) | Duloxetine delayed-release (60 mg/day)b | 25.1 (7.18) | -12.8 (0.68) | -4.4 (-6.2, -2.5) |
| Duloxetine delayed-release (120 mg/day)b | 25.1 (7.24) | -12.5 (0.67) | -4.1 (-5.9, -2.3) | |
| Placebo | 25.8 (7.66) | -8.4 (0.67) | -- | |
| Study2 (HAM-A) | Duloxetine delayed-release (60-120 mg/day)b | 22.5 (7.44) | -8.1 (0.70) | -2.2 (-4.2, -0.3) |
| Placebo | 23.5 (7.91) | -5.9 (0.70) | -- | |
| Study 3 (HAM-A) | Duloxetine delayed-release (60-120 mg/day)b | 25.8 (5.66) | -11.8 (0.69) | -2.6 (-4.5, -0.7) |
| Placebo | 25.0 (5.82) | -9.2 (0.67) | -- | |
| Study 5 (Elderly) (HAM-A) | Duloxetine delayed-release (60-120 mg/day)b | 24.6 (6.21) | -15.9 (0.63) | -4.2 (-5.9, -2.5) |
| Placebo | 24.5 (7.05) | -11.7 (0.67) | -- | |
| Study 6 (Pediatric) (PARS for GAD) | Duloxetine delayed-release (30-120 mg/day)b | 17.5 (1.98) | -9.7 (0.50) | -2.7 (-4.0, -1.3) |
| Placebo | 17.4 (2.24) | -7.1 (0.50) | -- | |
Figure 2: Kaplan-Meier Estimation of Cumulative Proportion of Patients with Relapse (GAD Study 4)
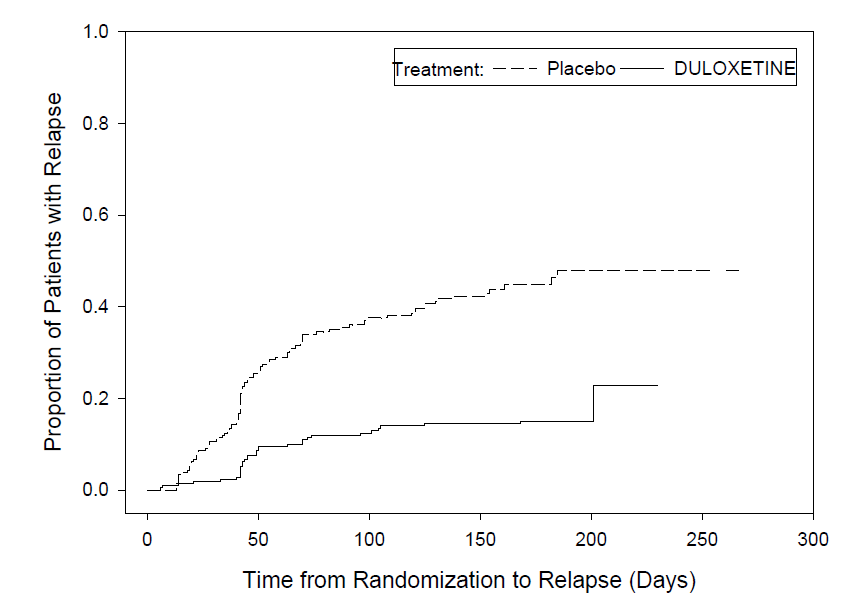
14.3 Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules for the management of neuropathic pain associated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy was established in 2 randomized, 12 week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, fixed-dose studies in adult patients having diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain for at least 6 months. Study DPNP-1 and Study DPNP-2 enrolled a total of 791 patients of whom 592 (75%) completed the studies. Patients enrolled had Type I or II diabetes mellitus with a diagnosis of painful distal symmetrical sensorimotor polyneuropathy for at least 6 months. The patients had a baseline pain score of ≥4 on an 11 point scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). Patients were permitted up to 4 g of acetaminophen per day as needed for pain, in addition to duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Patients recorded their pain daily in a diary. Both studies compared duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg once daily or 60 mg twice daily with placebo. DPNP-1 additionally compared duloxetine delayed-release capsules 20 mg with placebo. A total of 457 patients (342 duloxetine delayed-release capsules, 115 placebo) were enrolled in DPNP-1 and a total of 334 patients (226 duloxetine delayed-release capsules, 108 placebo) were enrolled in DPNP-2. Treatment with duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg one or two times a day statistically significantly improved the endpoint mean pain scores from baseline and increased the proportion of patients with at least a 50% reduction in pain scores from baseline. For various degrees of improvement in pain from baseline to study endpoint, Figures 3 and 4 show the fraction of patients achieving that degree of improvement. The figures are cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned 0% improvement. Some patients experienced a decrease in pain as early as week 1, which persisted throughout the study.Figure 3: Percentage of Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief as Measured by 24-Hour Average Pain Severity - DPNP-1
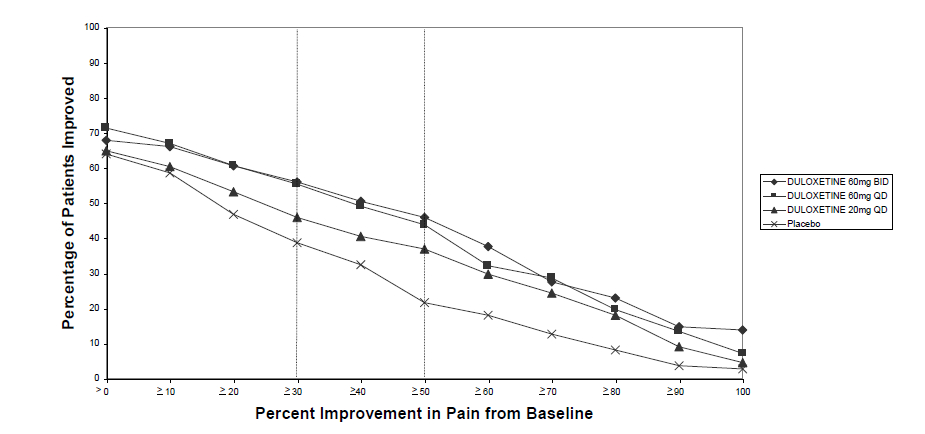
Figure 4: Percentage of Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief as Measured by 24-Hour Average Pain Severity - DPNP-2
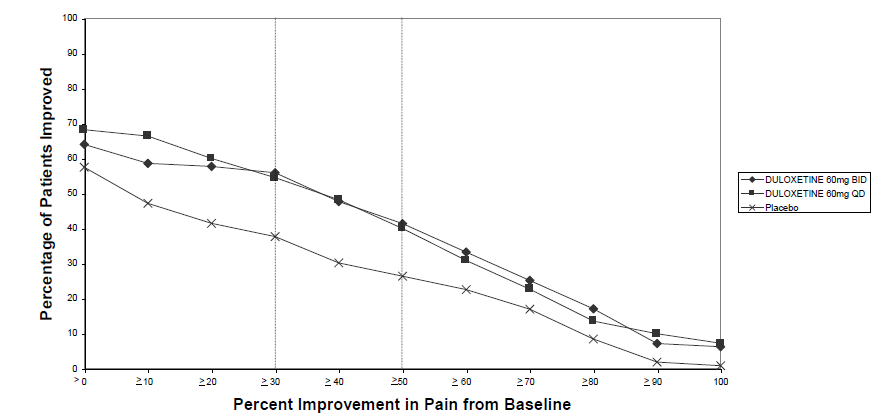
14.4 Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain
Duloxetine is indicated for the management of chronic musculoskeletal pain. This has been established in studies in patients with chronic low back pain and chronic pain due to osteoarthritis.Studies in Chronic Low Back Pain
The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in chronic low back pain (CLBP) was assessed in two double-blind, placebo- controlled, randomized clinical trials of 13 weeks duration (Study CLBP-1 and Study CLBP-2), and one of 12 weeks duration (CLBP-3). CLBP-1 and CLBP-3 demonstrated efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in the treatment of chronic low back pain. Patients in all studies had no signs of radiculopathy or spinal stenosis. Study CLBP-1: Two hundred thirty six adult patients (N = 115 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules, N = 121 on placebo) enrolled and 182 (77%) completed 13 week treatment phase. After 7 weeks of treatment, duloxetine delayed-release capsules patients with less than 30% reduction in average daily pain and who were able to tolerate duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg once daily had their dose of duloxetine delayed-release capsules, in a double-blinded fashion, increased to 120 mg once daily for the remainder of the study. Patients had a mean baseline pain rating of 6 on a numerical rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). After 13 weeks of treatment, patients taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 to 120 mg daily had a significantly greater pain reduction compared to placebo. Randomization was stratified by the patients’ baseline NSAIDs-use status. Subgroup analyses did not indicate that there were differences in treatment outcomes as a function of NSAIDs use. Study CLBP-2: Four hundred and four patients were randomized to receive fixed doses of duloxetine delayed-release capsules daily or a matching placebo (N = 59 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules 20 mg, N = 116 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg, N = 112 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules 120 mg, N = 117 on placebo) and 267 (66%) completed the entire 13 week study. After 13 weeks of treatment, none of the three duloxetine delayed-release capsules doses showed a statistically significant difference in pain reduction compared to placebo. Study CLBP-3: Four hundred and one patients were randomized to receive fixed doses of duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg daily or placebo (N = 198 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules, N = 203 on placebo), and 303 (76%) completed the study. Patients had a mean baseline pain rating of 6 on a numerical rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). After 12 weeks of treatment, patients taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg daily had significantly greater pain reduction compared to placebo. For various degrees of improvement in pain from baseline to study endpoint, Figures 5 and 6 show the fraction of patients in CLBP-1 and CLBP-3 achieving that degree of improvement. The figures are cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned the value of 0% improvement.Figure 5: Percentage of Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief as Measured by 24-Hour Average Pain Severity – CLBP-1
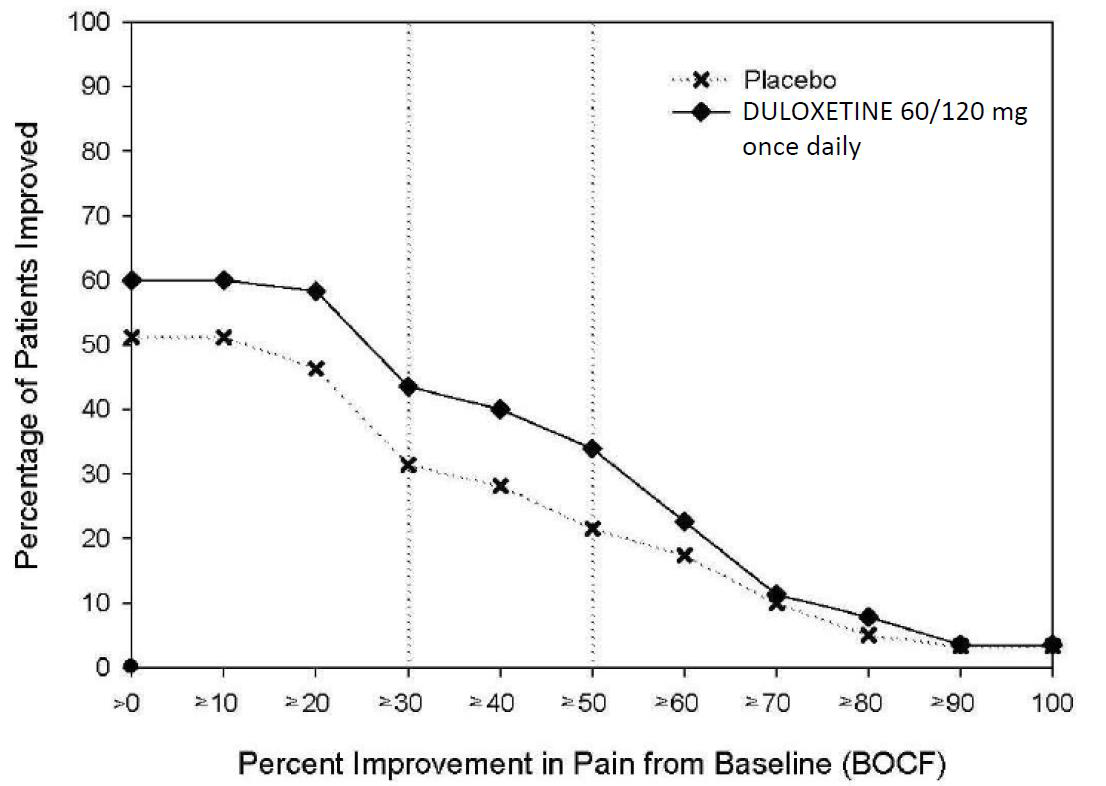
Figure 6: Percentage of Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief as Measured by 24-Hour Average Pain Severity – CLBP-3
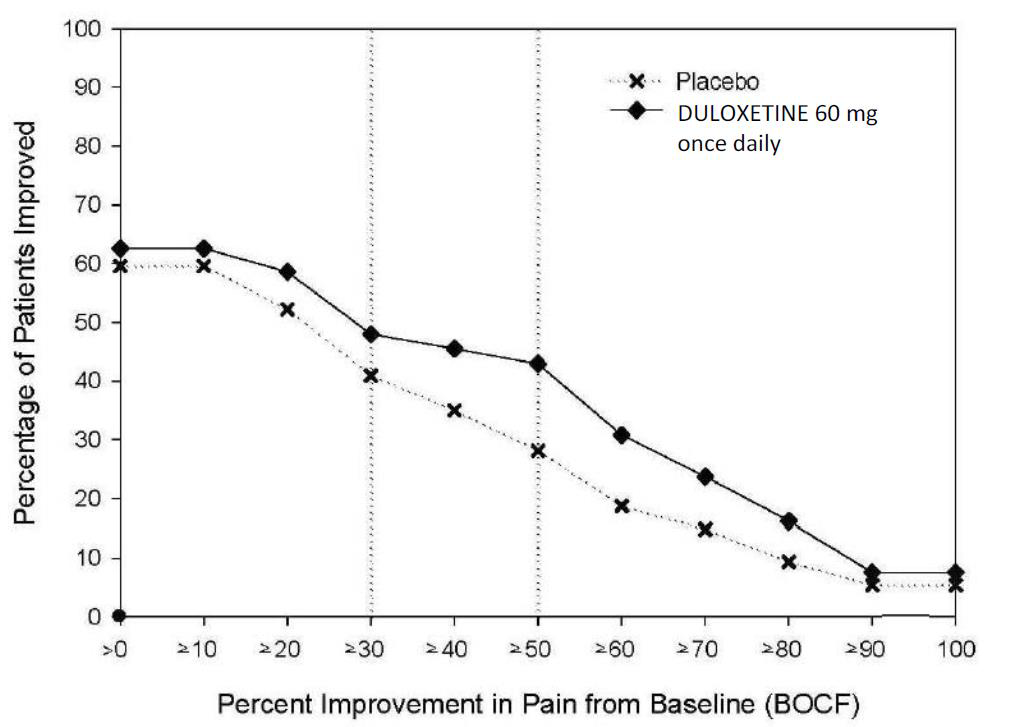
Studies in Chronic Pain Due to Osteoarthritis
The efficacy of duloxetine delayed-release capsules in chronic pain due to osteoarthritis was assessed in 2 double-blind, placebo- controlled, randomized clinical trials of 13 weeks duration (Study OA-1 and Study OA-2). All patients in both studies fulfilled the ACR clinical and radiographic criteria for classification of idiopathic osteoarthritis of the knee. Randomization was stratified by the patients’ baseline NSAIDs-use status. Patients assigned to duloxetine delayed-release capsules started treatment in both studies at a dose of 30 mg once daily for one week. After the first week, the dose of duloxetine delayed-release capsules was increased to 60 mg once daily. After 7 weeks of treatment with duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg once daily, in OA-1 patients with sub-optimal response to treatment (<30% pain reduction) and tolerated duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg once daily had their dose increased to 120 mg. However, in OA-2, all patients, regardless of their response to treatment after 7 weeks, were re-randomized to either continue receiving duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg once daily or have their dose increased to 120 mg once daily for the remainder of the study. Patients in the placebo treatment groups in both studies received a matching placebo for the entire duration of studies. For both studies, efficacy analyses were conducted using 13 week data from the combined duloxetine delayed-release capsules 60 mg and 120 mg once daily treatment groups compared to the placebo group. Study OA-1: Two hundred fifty six patients (N = 128 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules, N = 128 on placebo) enrolled and 204 (80%) completed the study. Patients had a mean baseline pain rating of 6 on a numerical rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). After 13 weeks of treatment, patients taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules had significantly greater pain reduction. Subgroup analyses did not indicate that there were differences in treatment outcomes as a function of NSAIDs use. Study OA-2: Two hundred thirty one patients (N = 111 on duloxetine delayed-release capsules, N = 120 on placebo) enrolled and 173 (75%) completed the study. Patients had a mean baseline pain of 6 on a numerical rating scale ranging from 0 (no pain) to 10 (worst possible pain). After 13 weeks of treatment, patients taking duloxetine delayed-release capsules did not show a significantly greater pain reduction. In Study OA-1, for various degrees of improvement in pain from baseline to study endpoint, Figure 7 shows the fraction of patients achieving that degree of improvement. The figure is cumulative, so that patients whose change from baseline is, for example, 50%, are also included at every level of improvement below 50%. Patients who did not complete the study were assigned the value of 0% improvement.Figure 7: Percentage of Patients Achieving Various Levels of Pain Relief as Measured by 24-Hour Average Pain Severity – OA-1
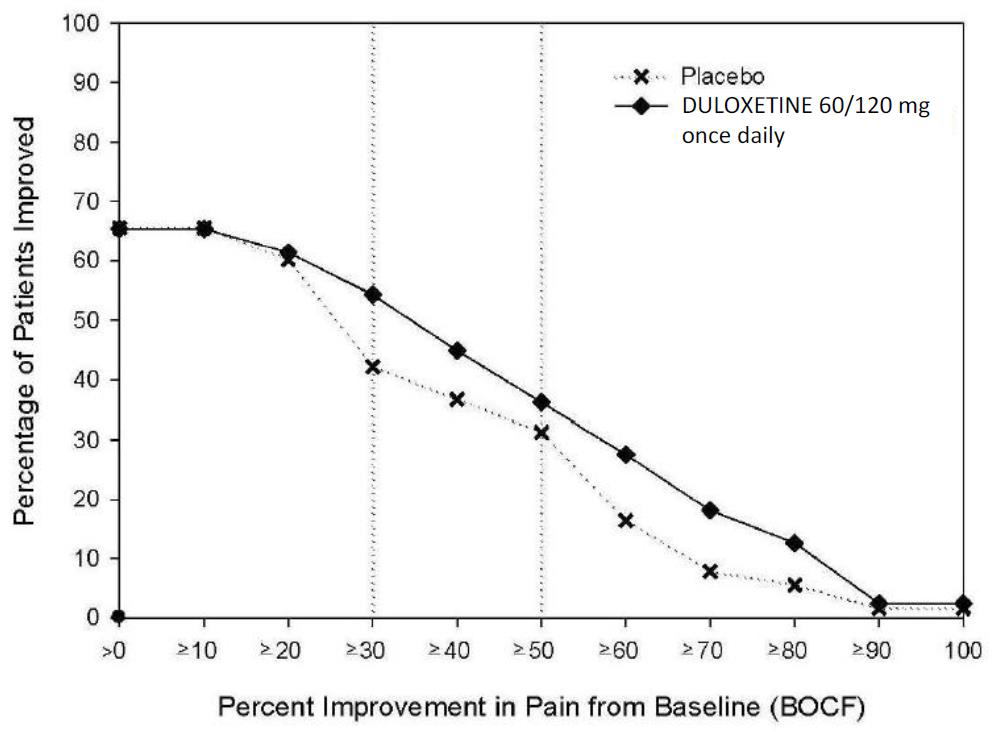
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
DRIZALMA Sprinkle (duloxetine delayed-release capsules) are available as follows:| Features | Strengths | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 mg a | 30 mg a | 40 mg a | 60 mg a | |
| Body color | Green | White | White | Green |
| Cap color | Green | Blue | White | Blue |
| Cap imprint | RG53 | RG54 | RL85 | RG55 |
| Body imprint | RG53 | RG54 | RL85 | RG55 |
| Presentations and NDC Codes | ||||
| Bottles of 30 | 47335-616-30 | 47335-617-30 | 47335-618-30 | 47335-619-30 |
| Bottles of 60 | 47335-616-60 | 47335-617-60 | 47335-618-60 | 47335-619-60 |
| Bottles of 90 | 47335-616-90 | 47335-617-90 | 47335-618-90 | 47335-619-90 |
| Bottles of 1000 | 47335-616-10 | 47335-617-10 | 47335-618-10 | 47335-619-10 |
16.2 Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Dispense in a tightly closed container. For 30, 60, and 90 count bottles only: This package is child-resistant.17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide and Instructions for Use). Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors - Advise families and caregivers of patients to look for the emergence suicidality, especially early during treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down, and instruct them to report such symptoms to the healthcare provider [see Boxed Warning, and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Hepatotoxicity - Inform patients that severe liver problems, sometimes fatal, have been reported in patients treated with duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Instruct patients to talk to their healthcare provider if they develop itching, right upper belly pain, dark urine, or yellow skin/eyes while taking DRIZALMA Sprinkle which may be signs of liver problems. Instruct patients to talk to their healthcare provider about their alcohol consumption. Use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle with heavy alcohol intake may be associated with severe liver injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Alcohol - Although duloxetine delayed-release capsules does not increase the impairment of mental and motor skills caused by alcohol, use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle concomitantly with heavy alcohol intake may be associated with severe liver injury. For this reason, DRIZALMA Sprinkle should not be prescribed for patients with substantial alcohol use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Orthostatic Hypotension, Falls and Syncope - Advise patients of the risk of orthostatic hypotension, falls and syncope, especially during the period of initial use and subsequent dose escalation, and in association with the use of concomitant drugs that might potentiate the orthostatic effect of DRIZALMA Sprinkle [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. Serotonin Syndrome - Caution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome with the concomitant use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle and other serotonergic agents including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, buspirone, tryptophan, amphetamines, and St. John’s Wort [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.4), and Drug Interactions (7)]. Advise patients of the signs and symptoms associated with serotonin syndrome that may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular changes (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). Caution patients to seek medical care immediately if they experience these symptoms. Increased Risk of Bleeding - Caution patients about the concomitant use of DRIZALMA Sprinkle and NSAIDs, aspirin, warfarin, or other drugs that affect coagulation since combined use of psychotropic drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and these agents has been associated with an increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Severe Skin Reactions - Caution patients that DRIZALMA Sprinkle may cause serious skin reactions. This may need to be treated in a hospital and may be life-threatening. Counsel patients to call their doctor right away or get emergency help if they have skin blisters, peeling rash, sores in their mouth, hives, or any other allergic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]. Discontinuation of Treatment - Instruct patients that discontinuation of DRIZALMA Sprinkle may be associated with symptoms such as dizziness, headache, nausea, diarrhea, paresthesia, irritability, vomiting, insomnia, anxiety, hyperhidrosis, and fatigue, and should be advised not to alter their dosing regimen, or stop taking DRIZALMA Sprinkle without consulting their physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]. Activation of Mania or Hypomania - Adequately screen patients with depressive symptoms for risk of bipolar disorder (e.g. family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression) prior to initiating treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle. Advise patients to report any signs or symptoms of a manic reaction such as greatly increased energy, severe trouble sleeping, racing thoughts, reckless behavior, talking more or faster than usual, unusually grand ideas, and excessive happiness or irritability [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. Angle-Closure Glaucoma - Advise patients that taking DRIZALMA Sprinkle can cause mild pupillary dilation, which in susceptible individuals, can lead to an episode of angle-closure glaucoma. Pre-existing glaucoma is almost always open-angle glaucoma because angle-closure glaucoma, when diagnosed, can be treated definitively with iridectomy. Open-angle glaucoma is not a risk factor for angle-closure glaucoma. Patients may wish to be examined to determine whether they are susceptible to angle-closure, and have a prophylactic procedure (e.g., iridectomy), if they are susceptible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Seizures - Advise patients to inform their physician if they have a history of seizure disorder [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]. Effects on Blood Pressure - Caution patients that DRIZALMA Sprinkle may cause an increase in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. Concomitant Medications - Advise patients to inform their physicians if they are taking, or plan to take, any prescription or over-the-counter medications, since there is a potential for interactions [see Dosage and Administration (2.10), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.12), and Drug Interactions (7)]. Hyponatremia - Advise patients that hyponatremia has been reported as a result of treatment with SNRIs and SSRIs, including duloxetine delayed-release capsules. Advise patients of the signs and symptoms of hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]. Concomitant Illnesses - Advise patients to inform their physicians about all of their medical conditions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]. DRIZALMA Sprinkle are in a class of medicines that may affect urination. Instruct patients to consult with their healthcare provider if they develop any problems with urine flow [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].Pregnancy and Lactation
- Advise patients to notify their healthcare provider if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during treatment with DRIZALMA Sprinkle.
- Advise patients that DRIZALMA Sprinkle use late in pregnancy may increase the risk of neonatal complications requiring prolonged hospitalization, respiratory support and tube feeding.
- Advise women that there is a risk of relapse with discontinuation of antidepressants.
- Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to antidepressants during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
- Advise patient to notify their healthcare providers if they are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
